Peer Review of Assessment is an external review process that is undertaken in collaboration with discipline experts from universities across the sector. Peer Review of Assessment supports Charles Sturt and other universities in meeting the Higher Education Standards Framework (Threshold Standards) 2021 requirement to:
Review and improve learning and teaching activities including regular external referencing of the success of student cohorts against comparable courses of study, including: the assessment methods and grading of students’ achievement of learning outcomes for selected units of study within courses of study.
Higher Education Standards Framework (Threshold Standards) 2021, Section 5.3 Monitoring, Review and Improvement
The HESF 2021 requires all higher education providers to undertake comprehensive course reviews at least every seven years and must include external referencing or other benchmarking activities. The purpose of the Peer Review of Assessment process is to improve the quality of our curriculum by providing a mechanism for a review and feedback for selected subjects on:
The process aims to provide a comparable review and constructive feedback about the standard of assessment tasks and the suitability of assessment tasks for supporting the achievement of learning outcomes in selected subjects. The outcomes of the Peer Review of Assessment provide evidence to inform quality enhancement to subjects and accrediting bodies for the assurance of learning.
Systematic quality improvement: Provides a structured and measurable approach to enhancing quality, ensuring organised and focused efforts for consistent and sustainable improvements.
External focus: Encourages looking beyond internal processes and outcomes by comparing practices with industry leaders and competitors, helping identify improvement areas.
Identification of best practices: Highlights effective practices that can be integrated to enhance operational efficiency and overall performance.
Exposes need for change: Offers a clear picture of where an organisation stands compared to peers and industry standards, highlighting specific areas requiring improvement.
Promotes contacts and networks: Engaging in this activity facilitates connections with other professionals and institutions, leading to valuable collaborations, partnerships, and knowledge-sharing opportunities.

| Step | Responsibility | Details | |
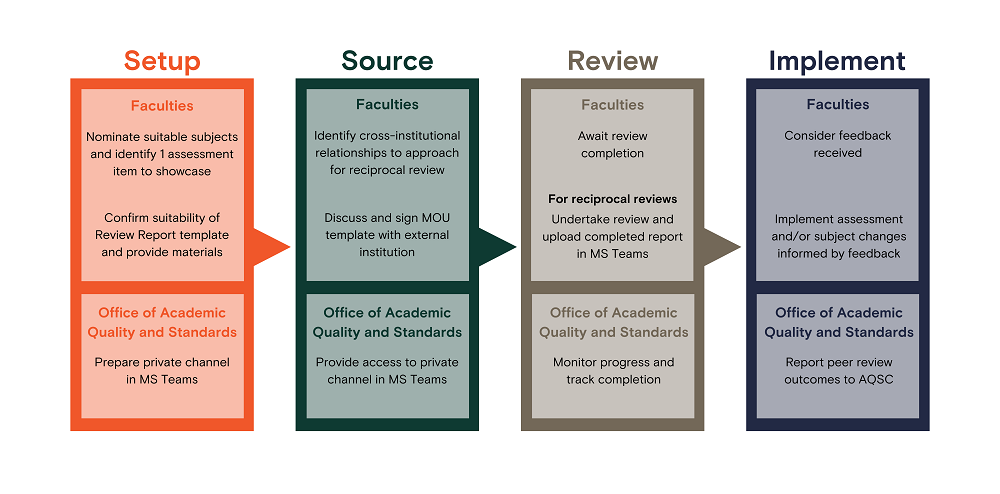
| 1 | Associate Dean (Academic) nominates suitable subject, including details of Subject Coordinator | Faculty | Faculties provide suitable subjects and Subject Coordinator details to OAQS. Refer to Choosing subjects section for more information. It is anticipated that Faculties nominate ten (10) subjects for peer review each year. |
| 2 | Identify cross-institutional relationships for potential reciprocal review | Faculty | Include when nominating subjects, so the OAQS can approach the institutions to propose a reciprocal review. |
| 3 | Identify one (1) assessment item to showcase | Faculty | For each subject nominated, one (1) or more assessment item is to be showcased. This would normally be the highest-weighted item. |
| 4 | Confirm or revise the standard Peer Review of Assessment Report template for suitability |
Faculty OAQS | This template can be tailored to suit the needs of each review, or to meet requirements of professional accrediting bodies. |
| 5 | Source five (5) student work samples | Faculty | For each showcased assessment item, five (5) samples of student work are required. Refer to the Materials required section for more information. |
| 6 | Consider any other review materials | Faculty | Any resources additional to the Subject Outline (i.e. graphs, calculations, templates, solutions file etc.) that will assist the reviewer in understanding the assessment requirements. |
| 7 | In cases of reciprocal reviews, sign a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with external institution | Faculty | If a reciprocal review is arranged, Faculties should discuss and sign the approved Peer Review of Assessment MOU template with the external institution. Band 6 (HOS) is authorised to sign the MOU. |
| 8 | Prepare private channel in MS Teams: CSU-Peer Review of Assessment | OAQS | Set up private channel for the review. Includes personalised welcome for external institution, resources and folder structure for file sharing. Refer to FAQs section for more information. |
| 9 | Communicate access and instructions to external reviewer and relevant Charles Sturt academic staff | OAQS | Once the private channel is ready, access and instructions are communicated via email to all parties for progressing the review. |
| 10 | Upload review materials |
Faculty External institution | Both parties (if reciprocal) use the prepared folder structure to upload review materials. OAQS can support this task if required. |
| 11 | Undertake review |
Faculty External institution | Using the agreed Review Report template and provided materials, both parties (if reciprocal) complete the review within the agreed time frame. |
| 12 | Upload Review Report |
Faculty External institution | Completed Review Reports are to be uploaded to the relevant folder in the private channel. |
| 13 | Consider feedback and implement changes | Faculty | Consider any feedback and recommendations made by the reviewer. In alignment with the Course and Subject Quality Assurance and Review Procedure, the reflections and decisions need to be recorded as an action item in QUASAR. The Subject Coordinator should also write a reflective statement to record as ‘Scholarly Activities in Learning and Teaching reflection’ in the Charles Sturt University Research Output (CRO) system. |
| 14 | Outcomes reported to AQSC |
OAQS Faculty | In consultation with Faculties, outcomes resulting from peer reviews are reported to AQSC in August each year as part of the Subject Quality Enhancement and Grade Distribution Monitoring Report. |
Review questions can be tailored to suit the criteria of the accrediting body
Faculties are asked to source and provide the following materials for each nominated subject:
Charles Sturt subject
It is recommended that the academic staff member allow 2 hours (per subject) to source and provide the required materials noted above. Following completion of the review activity, further time will be required for reflection on feedback received, implementation of changes informed by this feedback, and reporting.
Other institution subject
When our subjects are being reviewed by way of a reciprocal review arrangement with another institution, the expected time commitment for a Charles Sturt academic staff member to review an external subject may differ from one institution to another. The complexity of assessment, the length of student samples, and the format of the institution’s Review Report template are all contributing factors to this varying time commitment.
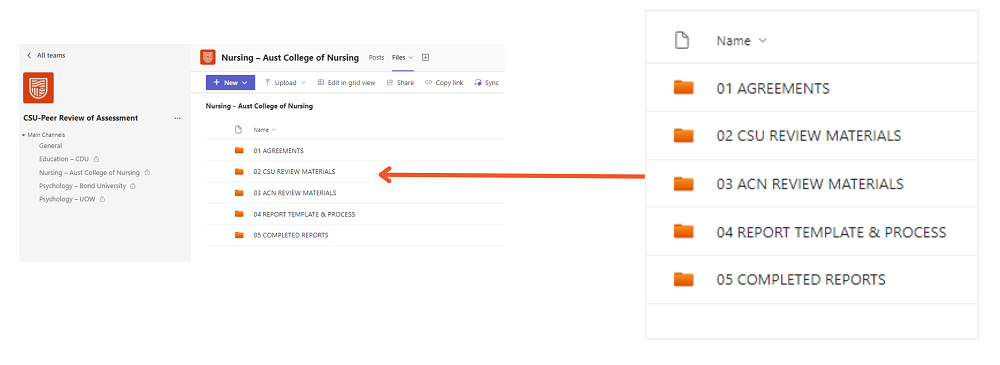
Reviews are facilitated through a collaborative space in MS Teams, with the capability to grant access to external institutions. This platform is established, and a new private channel is added for each new institution we engage to complete a review. The OAQS sets up each private channel with access to relevant staff from both Charles Sturt and the external institution, then posts a welcome announcement and Review Process resource. The channel provides a common folder structure, for both parties to share and access files such as signed agreements (MOUs), review materials, Review Report template(s) and completed reports.
Example:
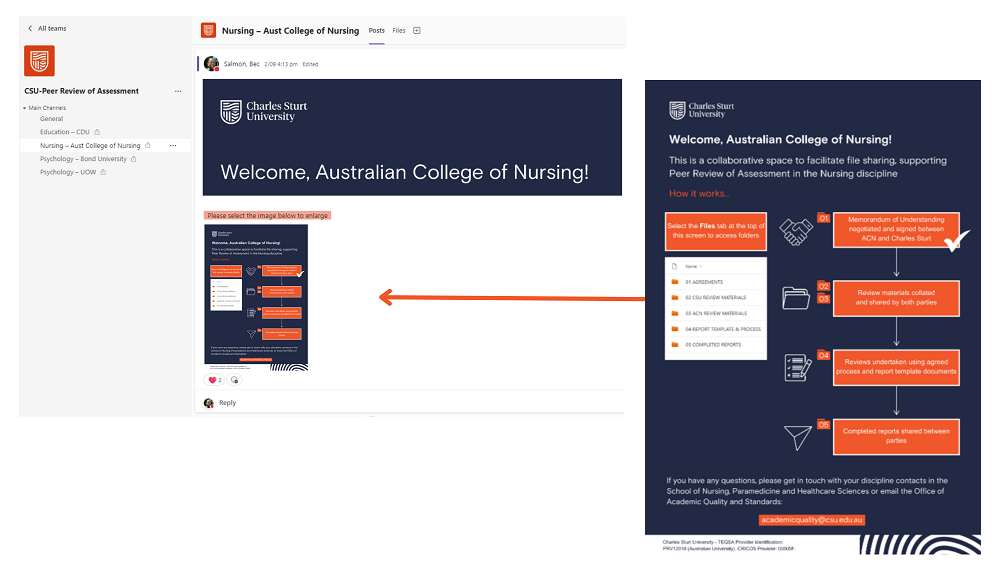
Please contact the Office of Academic Quality and Standards if any questions: academicquality@csu.edu.au
The Associate Dean (Academic) (ADA) in each Faculty has been appointed to liaise with the Office of Academic Quality and Standards to ensure this happens. Please contact the ADA in your Faculty for more information: